Upgrading Debian Version
Upgrading Debian from one version to the next is actually a simple, straight forward process. All you have to do is change the apt source repository from one Debian version to the next one, and update!
As with any major system upgrades, make sure you backup your configs and important files! If you are upgrading a VM, take a snapshot first.
Upgrading from Debian 11 Bullseye to Debian 12 Bookworm
First, check your Debian version by running the following command, or run neofetch if you have that installed:
cat /etc/os-release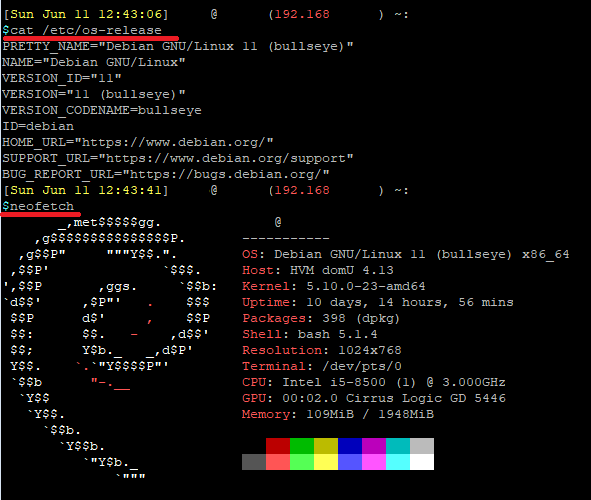
Next, make sure your current system is fully up to date.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y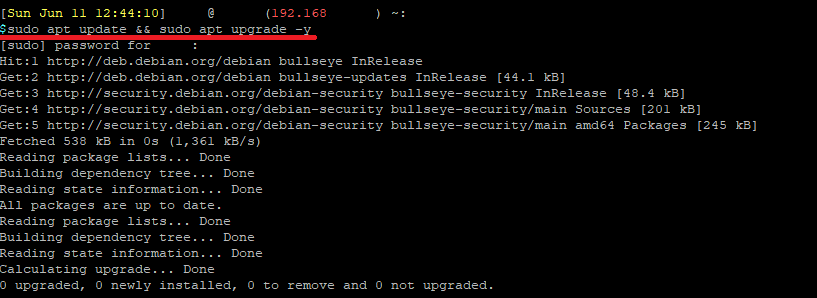
Check your current apt package manager source list:
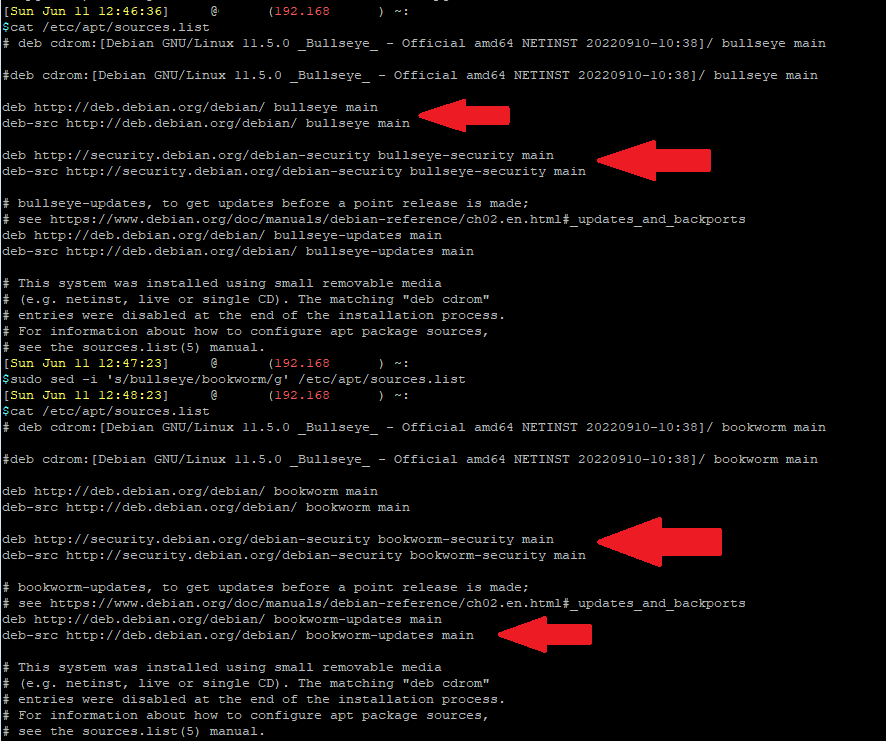
cat /etc/apt/sources.listYou will see that the source repository will say Bullseye (for Debian 11).
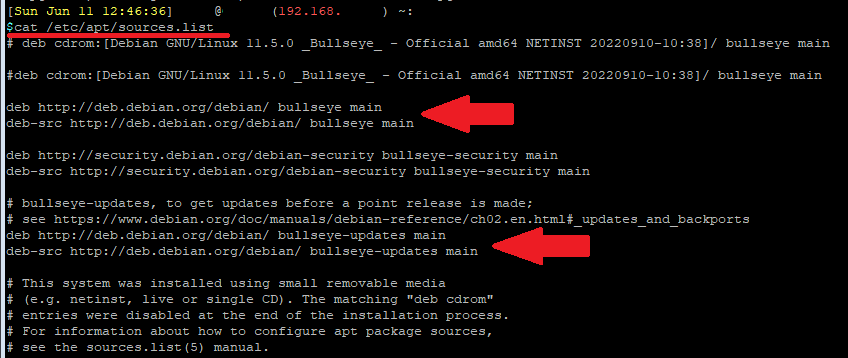
Upgrading Debian is as simple as replacing the current repository source (Bullseye) to the newer version's repository source (Bookworm). So in the above source file, replace all instance of "bullseye" with "bookworm" using an editor like nano, or run the following command to search and replace:
sudo sed -i 's/bookworm/trixie/g' /etc/apt/sources.listAfterwards, you can run "cat /etc/apt/sources.list" again to check that all instances of "bullseye" is replaced with "bookworm".
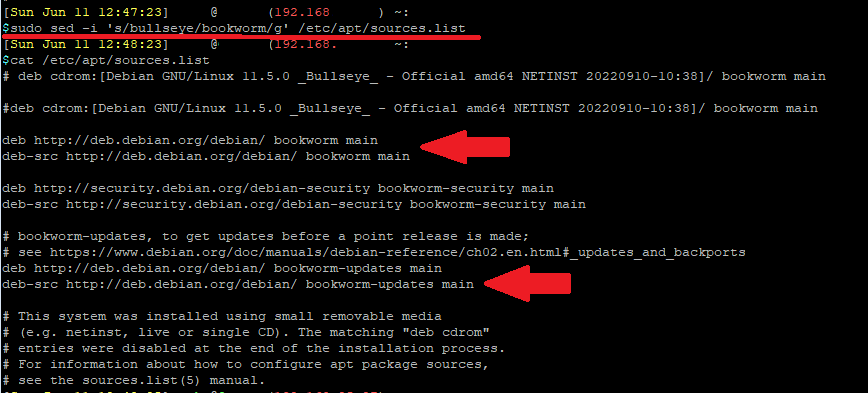
Now you can update the repository.
sudo apt update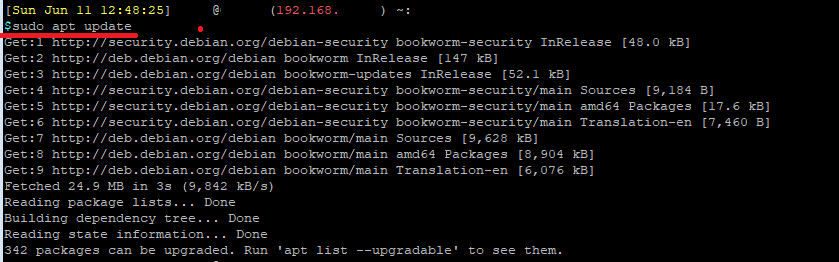
To start the upgrade, run the following:
sudo apt full-upgrade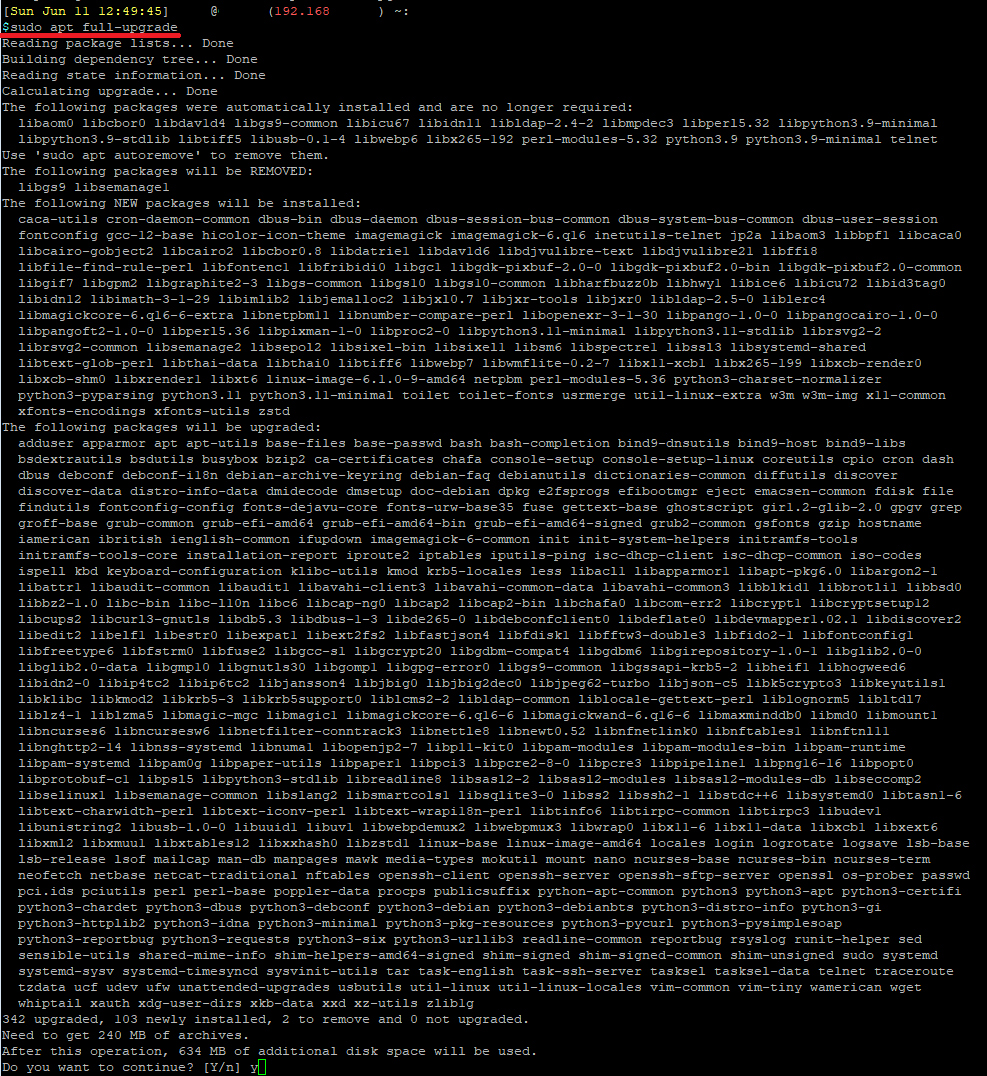
At some point in the upgrade process, you will be presented with the apt change list. Press Q to exit the change-list.
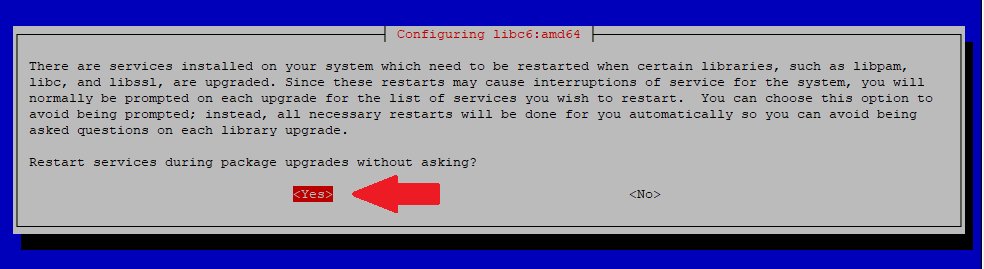
Choose Yes to allow the upgrade to auto-restart services.
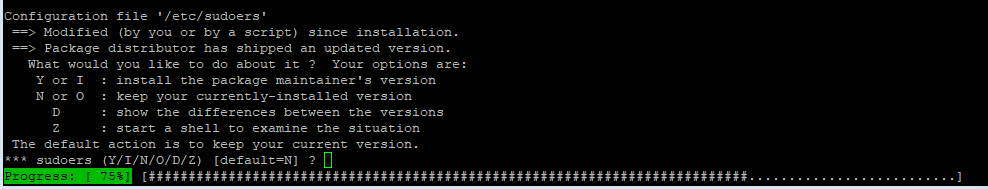
Type N to keep your current, customize config. Otherwise, you can type Y to reset and use the default config.
Once done, reboot your system.
sudo rebootAfter reboot, you can check that your system is upgraded by checking /etc/os-release, or run neofetch.
cat /etc/os-release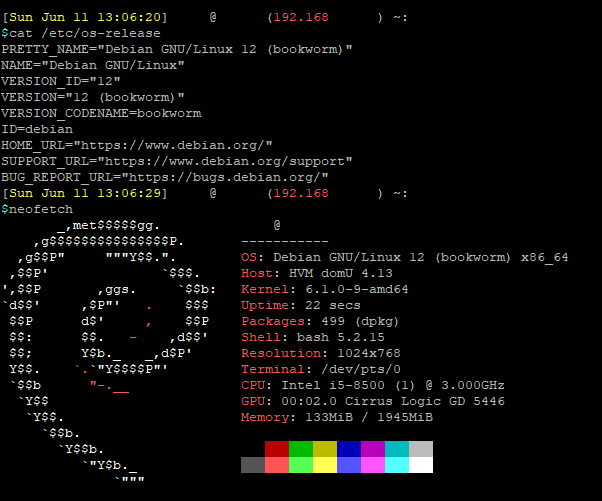
Lastly, you can run the following to remove any old and unnecessary packages:
sudo apt autoremove -y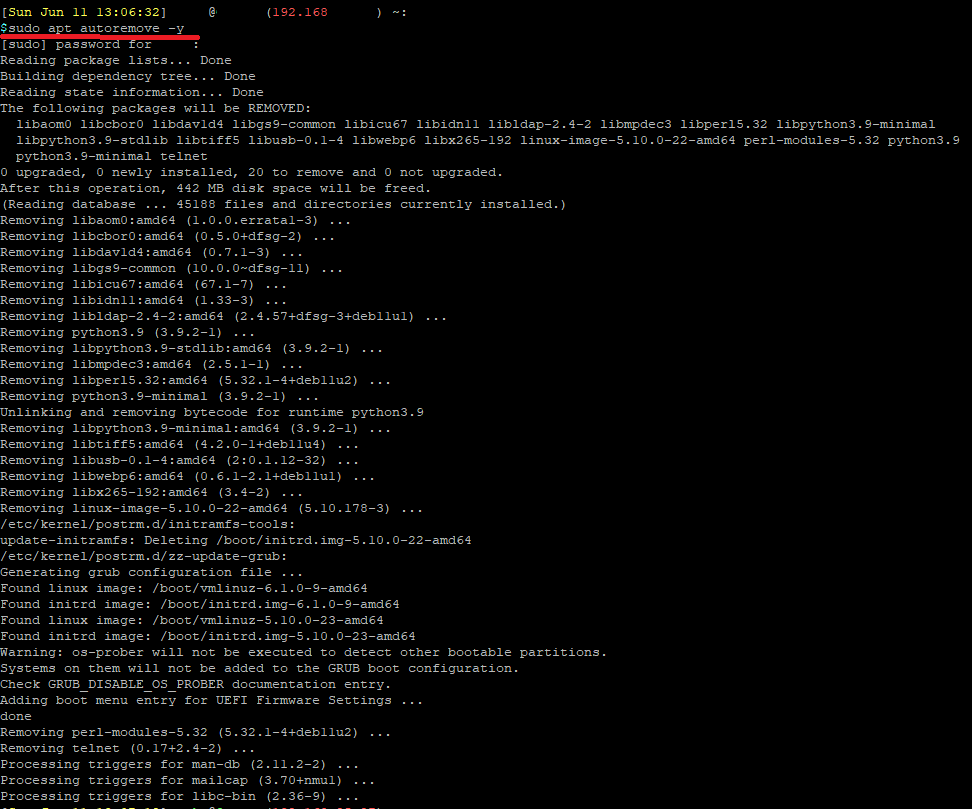
That's it!
